Background
@In the research fields, such as computer vision and intelligent robot control, there have been various researches where the relation between phenomena can be regarded as causal relationship based on a physical law, and expressed by a mathematical model. However, if we try to describe various phenomena in the real world based on the such approach, we face the following problems:
- We need a very complicated law or numerous rules to describe the relation.
- There are many phenomena which are very difficult to explain by casual relationships that are intrinsic in such phenomena.
As a result, we have not yet been able to build the system which realizes intelligent behaviors in the real world. Though causal relationship between phenomena is mostly unknown, we can only estimate the correlation between phenomena from real examples of the phenomena. Therefore, we can realize intelligent behavior of the system in the real world to a certain amount of level, by learning correlation between phenomena rather than expressing those causal relationship with a mathematical model. Generally, such correlation can be regared as a nonlinear mapping between arbitrary dimensional spaces.
Drawbacks in the previous work
There have been many methods for learning the nonlinear mapping, such as the neural network (NN) method, the Group Method of DataHandling (GMDH) method, the RBF network (RBFnet) method and the NGnet method. In addition to these methods, there have been learning methods based on memorizing all events caused by a phenomenon, such as k-nearest neighbor (k-NN) method. However, we have faced the following problems so far:
- Regarding NN/GMDH/RBFnet/NGnet method, some parameters for determining the structure of a learning system must be set up in advance. Unless initial values are set up appropriately, it is impossible for these methods to estimate a complicated mapping. Furthermore, there is no guarantee that the estimation accuracy of a nonlinear mapping is under a threshold for every data.
- Regarding k-NN method, we need a long time to search k-nearest neighbors and then estimate a mapping based on such neighbor data if an event is expressed by high-dimensional variables. Furthermore, we need a large amount of memories to store a lot of data as it is.
Basic idea and Advantages
We developed a versatile regression tree algorithm which can represents a nonlinear mapping between arbitrary dimensional spaces, and can achieve the reliable estimation of the objective mapping. Providing a feasible error threshold and training samples, our method automatically divides the objective mapping into partially linear mappings. In order to estimate the most reliable linear mappings satisfying the feasible error criterion, we employ split-and-merge strategy for the decomposition. Due to such strategy, our method doesn't spend long time to split an input hyperspace, and to construct a regression tree for estimating a complicated mapping. Since decomposed mappings are maintained by a binary tree, the linear mapping corresponding to an input is quickly calculated. We call this method a ''Partially Linear Mapping tree (PaLM-tree).''
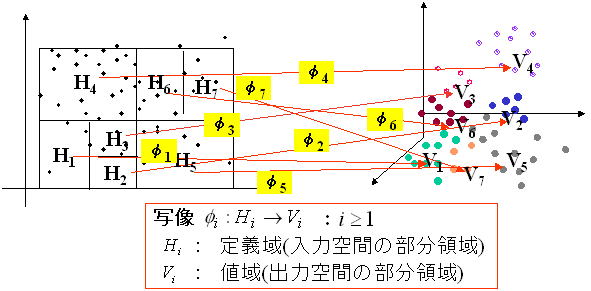
PaLM-tree iteratively
divides the input hyperspace ![]() into smaller local hyperspaces with equal dimension each of
which is called gdomainh based on an estimation error. Hereafter, let
into smaller local hyperspaces with equal dimension each of
which is called gdomainh based on an estimation error. Hereafter, let ![]() and
and ![]() be a domain and
the range corresponding to the domain
be a domain and
the range corresponding to the domain ![]() , respectively. Then, it estimates each linear mapping
between
, respectively. Then, it estimates each linear mapping
between ![]() and
and ![]() by principal
components regression using a training data set
by principal
components regression using a training data set ![]() within each
domain
within each
domain ![]() and range
and range ![]() . If the estimation error of linear mapping is more than a
feasible threshold, it proceeds to divide the domain. Otherwise, it stops to
divide. As a result, it represents
the nonlinear mapping
. If the estimation error of linear mapping is more than a
feasible threshold, it proceeds to divide the domain. Otherwise, it stops to
divide. As a result, it represents
the nonlinear mapping ![]() between
between ![]() and
and ![]() by multiple
linear mappings
by multiple
linear mappings ![]()
In the PaLM-tree, decomposition of the input space is maintained by a binary
tree. The root of the tree does not have any incoming edges. Every other node
has one incoming edge and have two outgoing edges. We call a node without
outgoing edges a leaf node, otherwise is called an internal node. PaLM-tree divides an input hyperspace ![]() into regions
defined by axis-aligned hyperrectangles. A hyperrectangle (
into regions
defined by axis-aligned hyperrectangles. A hyperrectangle (![]() dimensional rectangle) is recursively subdivided into two hyperrectangles
with equal dimension. Each node of PaLM-tree is associated with a
hyperrectangle, and therefore it is implicitly associated with a set of
training samples lying within this hyperrectangle. In particular, each leaf node represents a final subdivision
of the input and output hyperspace.
dimensional rectangle) is recursively subdivided into two hyperrectangles
with equal dimension. Each node of PaLM-tree is associated with a
hyperrectangle, and therefore it is implicitly associated with a set of
training samples lying within this hyperrectangle. In particular, each leaf node represents a final subdivision
of the input and output hyperspace.
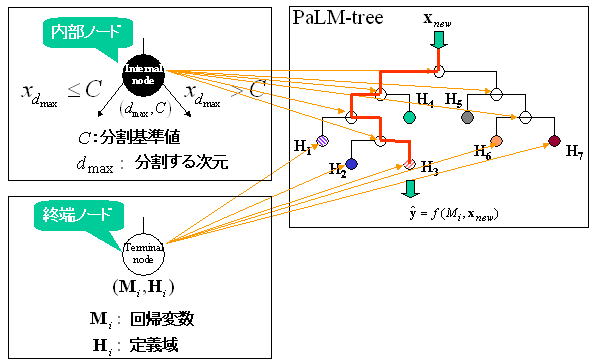
The PaLM-tree has attractive properties as follows:
- Against
NN, GMDH, RBFnet and Ngnet,
- It can gurantee that the estimated error become under the predefined threshold in every domains.
- It doesn't require complicated control parameters. It is provided with only a feasible error threshold.
- Against
k-NN,
- Its calculation time is faster than that of k-NN, because the height of the tree is low.
- It doesn't require a large amount of memories for estimating the output vectors because it only stores the linear regression parameters in the leaf nodes.
Example result
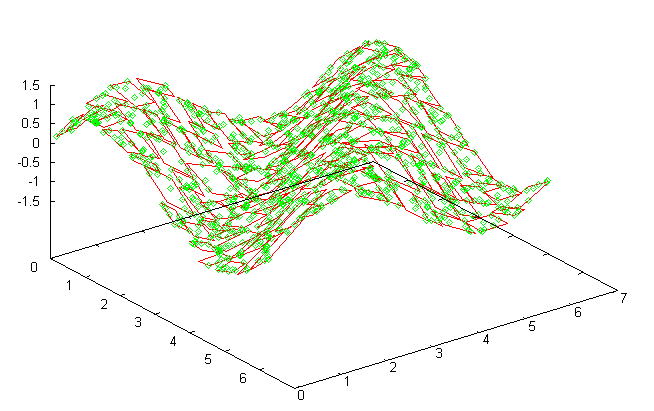
The following graph shows an examples of function
approximation by PaLM-tree. In this graph, the green points show the training
data that are generated by ![]() , a red patch shows the estimated local linear mapping.
, a red patch shows the estimated local linear mapping.
Application area
- Image segmentationiapplication to Computer Visionj
- Surveillance cameraiapplication to Computer Visionj
- Camera calibrationiapplication to Computer Visionj
- Learning forward and inverse model of a robot systemiapplication to Roboticsj
- Modeling reflection characteristic of an objectiapplication to Computer graphicsj
- Multi-class classifier iapplication to Pattern recognitionj
It can be applied to various problems.
Reference
- T. Nakamura, E. Kato and T. Wada, hA novel nonlinear mapping method (PaLM-tree) and its applicationhCProc. Of 9th Robotics SymposiumCpp.360-366, 2004. [PDF] (written in Japanese).
- T. Kawahara, T. Nakamura and T. Wada, hMotion planning for wheeled mobile robots based on PaLM-treehCProc. Of Robotics Mechatronics 2004. 2P1-L1-27, 2004. [PDF] (written in Japanese).
Software
@If you are interested in using the PaLM-tree, please contact me (ntakayuk@sys.wakayama-u.ac.jp)
by e-mail.
Attention !
This software is designed for the research communities. @We do not make
any warranty as to the results that may be obtained from the use of this
software and do not take any responsibility for them.
- Linux version (CLAPACK is required.)
- Windows versioniCLAPACK is required. Use VC++6.0 or gcc on Cygwin for compilej